The 21st century has brought with it a new space race. With the world’s leading space agencies now equipped with powerful new megarockets, the race is on to establish a base on the moon. The US space agency, NASA, is among the frontrunners in this new frontier and has set its sights on the lunar south pole.
Why the Moon’s South Pole?
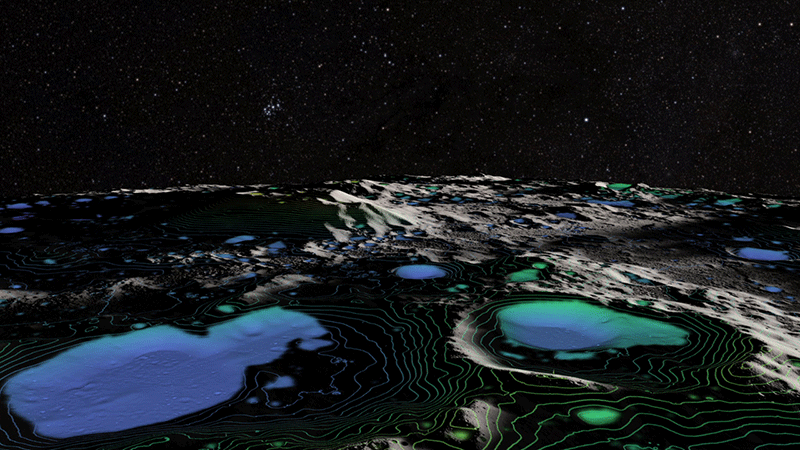
The moon’s south pole is one of the most extreme places in the solar system, with lightless craters that can plunge temperatures to minus 391 degrees Fahrenheit. Yet, it is also home to one of the most valuable resources in space – water. NASA believes that harvesting this ice is crucial to make drinkable water, oxygen, and fuel for rockets. With plans to land astronauts near craters in the lunar south pole as soon as 2025, the race to the moon is truly heating up.
The Legal Landscape of Lunar Resources
Despite the excitement surrounding lunar resource extraction, the legal landscape of who can own and extract resources from the moon is still murky. The Outer Space Treaty, signed by many nations in the 1960s, prohibits any country from owning parts of space. However, the treaty is silent on the private sector and leaves many questions over lunar resources unanswered.

Recognition of Private
Extraction Four nations, the US, Luxembourg, Japan, and the United Arab Emirates, have laws that recognize the ability of private companies to extract resources from outer space. These laws follow the leading interpretation of international law governing the high seas, according to Frans von der Dunk, a professor of space law at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
NASA’s Artemis Accords
NASA has written and signed the Artemis Accords, broad, non-binding principles for cooperating peacefully in space that include a section on “Space Resources.” As of January 2023, 23 nations have signed the accords. The signatories note that the utilization of space resources can benefit humankind by providing critical support for safe and sustainable operations.
The Private Sector’s Role in Lunar Resource Extraction
While the legal landscape of lunar resources is still evolving, the private sector is set to play a significant role in the extraction of lunar resources. With companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin, the private sector has the capability to extract resources from the moon, and with it the potential to reap huge profits.
The Future of Lunar Resource Extraction
The future of lunar resource extraction is uncertain, with many questions still left unanswered. However, one thing is clear, the race to the moon is heating up, and whoever is able to establish a base on the lunar south pole will have a significant advantage in the new cosmic frontier.
Conclusion
The discovery of water on the moon has reignited the race to the moon and with it, the questions over who will be allowed to take what and where from the lunar south pole. The legal landscape of lunar resources is still evolving, with the private sector set to play a significant role in the extraction of resources from the moon. With NASA’s Artemis Accords and the recognition of private extraction by several nations, the future of lunar resource extraction is exciting and full of possibilities.